Quantitative Research Design
Quantitative Research Design
(Quantitative Research Design)
There are different types of quantitative research designs that justify or support themselves in nursing research.
Choose one quantitative type design and identify a major advantage and a major disadvantage of this design.
Give an example how this quantitative research design could be used in nursing practice to solve a clinical problem (not one noted in your textbook).
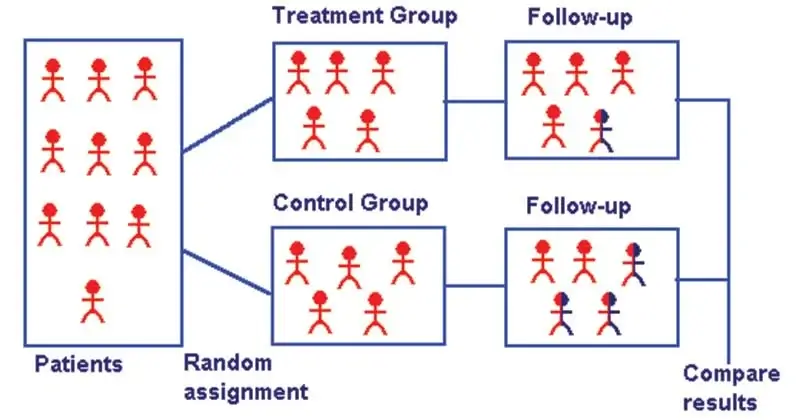
Quantitative Research Design: Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) are one of the most robust quantitative research designs used in nursing research. RCTs involve the random assignment of participants into experimental and control groups to assess the effectiveness of interventions.
Major Advantage:
One significant advantage of RCTs is the ability to minimize bias and confounding variables. Randomization ensures that the participants in each group are comparable, reducing the influence of external factors on the outcome. This enhances the internal validity of the study, allowing researchers to make strong causal inferences about the relationship between the intervention and the observed effects. As a result, findings from RCTs are considered the gold standard in evidence-based practice, helping clinicians make informed decisions about patient care.
Major Disadvantage:
However, a major disadvantage of RCTs is the potential for limited generalizability. The controlled environment in which RCTs are conducted may not reflect real-world clinical settings. Participants in RCTs often meet strict inclusion and exclusion criteria, which can result in a sample that is not representative of the broader population. Therefore, while RCTs provide high-quality evidence, the findings may not be applicable to all patient populations or clinical scenarios.
Example of RCT in Nursing Practice
An example of how RCTs could be used in nursing practice to solve a clinical problem is in the management of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Nurses often face challenges in improving patient adherence to prescribed inhalation therapies, which is critical for effective disease management.
Study Proposal:
An RCT could be designed to evaluate the effectiveness of a personalized education program on medication adherence among patients with COPD. In this study, participants would be randomly assigned to either an experimental group that receives personalized education sessions, including demonstrations of inhaler techniques and discussions about the importance of adherence, or a control group that receives standard education materials.
Outcome Measures:
The primary outcome measure could be the adherence rate to inhalation therapy, assessed using pharmacy refill records or self-reporting questionnaires. Secondary outcomes may include quality of life measures and the frequency of acute exacerbations.
Impact on Nursing Practice:
This RCT would provide valuable evidence on whether personalized education significantly improves adherence to inhalation therapy in COPD patients. If the intervention proves effective, it could lead to the implementation of similar educational programs in clinical practice, ultimately improving patient outcomes, reducing hospitalizations, and enhancing the overall quality of care for individuals with COPD. This approach highlights the important role of nurses in designing and implementing evidence-based interventions to address clinical challenges.
References
Fitzgerald, K. et al. (2020). “Evaluating the Effectiveness of a Patient Education Program for Inhaler Technique Among Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 52(2), 123-131. Available at:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jnu.12492
Cameron, A. et al. (2018). “The Effect of Educational Interventions on Medication Adherence in Patients with Chronic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.” BMC Health Services Research, 18(1), 32. Available at:
https://bmchealthserviceresearch.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-018-2895-6


