Kidney Disorder/Disease
5 pages write up on kidney disease
Kidney Disease: Understanding, Management, and Treatment
Kidney disease, also known as renal disease, encompasses a range of conditions that affect the kidneys’ ability to perform their critical functions, such as filtering waste products and maintaining fluid balance in the body. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the most prevalent form of kidney disease, gradually reducing kidney function over time. If left untreated, CKD can progress to kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is another significant kidney condition that occurs suddenly, typically as a result of severe illness or trauma. Kidney disease affects millions worldwide, contributing to a significant burden on healthcare systems. This paper will examine kidney disease, its causes, stages, symptoms, treatment options, and the importance of patient education and prevention. (Kidney Disorder/Disease)
Causes of Kidney Disease
Kidney disease can arise from a variety of causes, ranging from genetic predisposition to lifestyle factors. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is frequently caused by long-term conditions such as diabetes mellitus and hypertension, both of which damage the kidneys’ filtration system over time. According to a study by Thomas et al. (2019), diabetes accounts for approximately 40% of cases of CKD, while hypertension contributes to 25%. Both conditions impair blood flow to the kidneys, leading to glomerular damage and decreased filtration capacity.
Other causes of CKD include polycystic kidney disease, a genetic disorder that leads to the formation of cysts in the kidneys, and autoimmune diseases like lupus nephritis, which cause inflammation and damage to kidney tissues. Recurrent urinary tract infections and chronic obstruction from kidney stones can also contribute to kidney disease by causing repeated damage to the urinary system and kidney tissues (Levey et al., 2020).
Acute kidney injury (AKI), on the other hand, occurs suddenly, often as a result of a severe illness, infection, or trauma that temporarily impairs kidney function. AKI can be caused by dehydration, sepsis, or drug toxicity, particularly from nephrotoxic medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and certain antibiotics (Bellomo et al., 2019). While AKI is often reversible with timely intervention, severe cases can lead to chronic kidney damage. (Kidney Disorder/Disease)
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
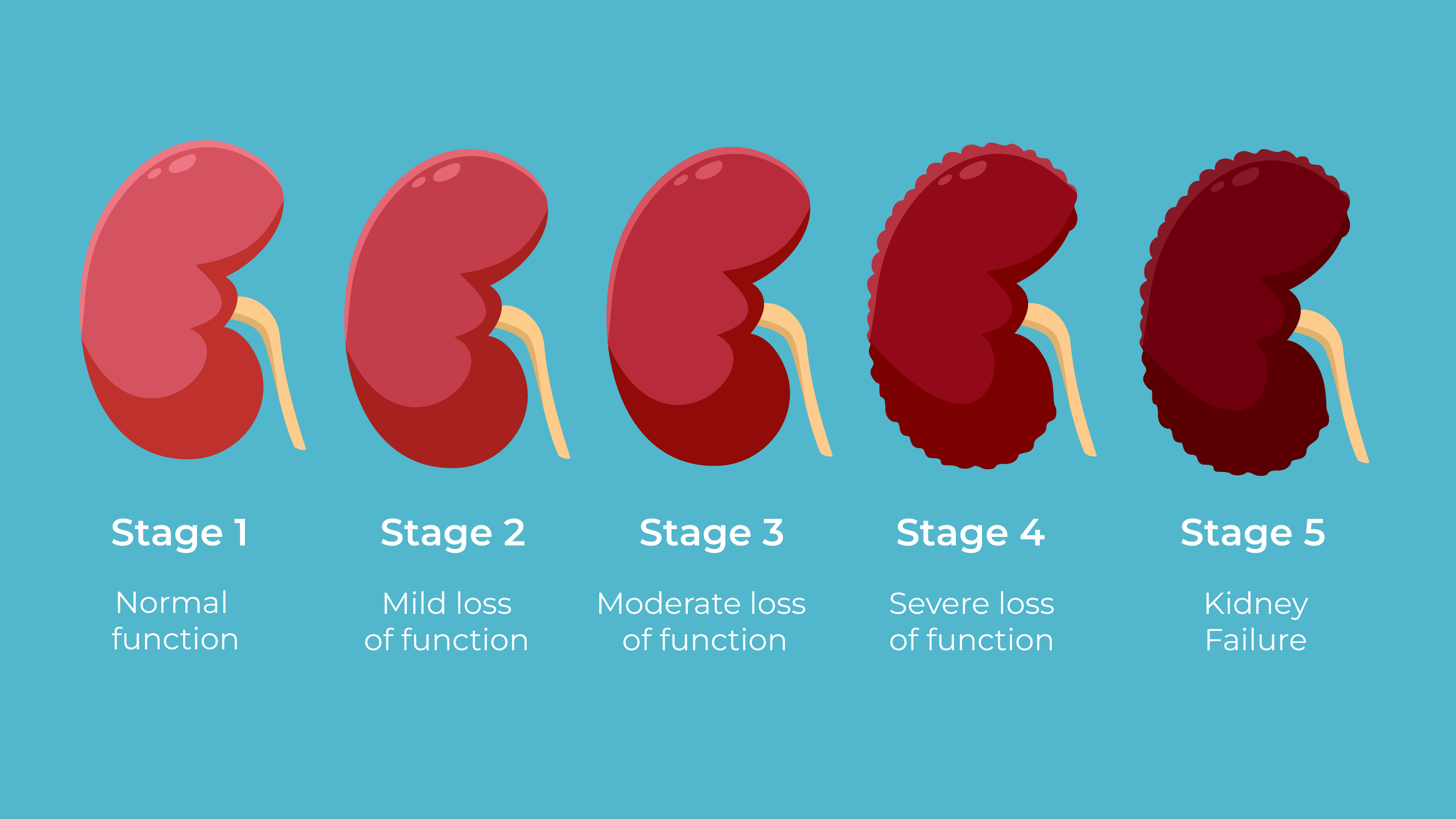
Chronic kidney disease progresses through five stages, based on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), which measures how well the kidneys are filtering blood. Stage 1 CKD is characterized by mild kidney damage with a normal eGFR of 90 or above, and patients may not exhibit symptoms. Early intervention at this stage, focusing on managing underlying conditions like diabetes and hypertension, can prevent progression (Levey et al., 2020).
In Stage 2 CKD, the eGFR drops to 60-89, indicating mild loss of kidney function. While symptoms may still be absent, regular monitoring of kidney function is crucial. Stage 3 CKD is divided into two sub-stages: 3a, with an eGFR of 45-59, and 3b, with an eGFR of 30-44. At this stage, patients may begin to experience symptoms such as fatigue, swelling, and changes in urination. The kidneys are less able to regulate electrolytes, leading to imbalances in sodium, potassium, and phosphorus levels (Luyckx et al., 2021).
In Stage 4 CKD, the eGFR declines to 15-29, indicating severe loss of kidney function. Patients may experience more pronounced symptoms such as fluid retention, anemia, and bone disease due to impaired vitamin D metabolism. At this stage, preparation for dialysis or a kidney transplant is often initiated. (Kidney Disorder/Disease)
Stage 5 CKD, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), occurs when the eGFR falls below 15. Kidney function is nearly or completely lost, and the patient requires dialysis or a kidney transplant to survive. Symptoms at this stage can be severe, including difficulty breathing, severe fatigue, and confusion due to the buildup of toxins in the blood. (Kidney Disorder/Disease)
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Kidney Disease
The symptoms of kidney disease often develop gradually and may not be noticeable until the condition has significantly progressed. Common symptoms include fatigue, swelling in the legs and ankles, changes in urination (such as increased or decreased frequency), and difficulty concentrating. Patients with advanced kidney disease may also experience muscle cramps, nausea, vomiting, and persistent itching due to the buildup of waste products in the blood (Levey et al., 2020).
Diagnosing kidney disease typically involves a combination of laboratory tests and imaging studies. A blood test measuring creatinine levels is used to estimate the glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), which provides an indication of kidney function. Urine tests are also conducted to check for proteinuria (excess protein in the urine), a sign of kidney damage. Imaging studies, such as ultrasounds or CT scans, may be used to assess the size and structure of the kidneys and detect any abnormalities (Levey et al., 2020).
Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
The treatment of kidney disease depends on the underlying cause, the stage of the disease, and the patient’s overall health. In the early stages of CKD, managing underlying conditions such as diabetes and hypertension is crucial to slowing disease progression. Medications such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are commonly prescribed to control blood pressure and reduce proteinuria, thereby protecting the kidneys from further damage (Luyckx et al., 2021).
In patients with more advanced CKD, additional treatments may be required to manage complications. For example, erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) can be used to treat anemia, while phosphate binders and vitamin D supplements help manage bone disease. Dietary modifications, including reducing sodium, potassium, and phosphorus intake, are often recommended to prevent electrolyte imbalances and slow kidney disease progression (Kalantar-Zadeh et al., 2020).
When kidney function declines to Stage 5 CKD, patients require dialysis or a kidney transplant. Dialysis, either through hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis, removes waste products and excess fluid from the blood, providing temporary relief from the symptoms of kidney failure. However, dialysis does not cure kidney disease, and patients often remain on dialysis for life unless they are eligible for a kidney transplant (Levey et al., 2020).
Prevention and Patient Education
Preventing kidney disease involves both lifestyle modifications and early detection of at-risk individuals. Promoting healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking, can reduce the risk of developing conditions like diabetes and hypertension, which are major contributors to kidney disease. Educating patients on the importance of managing these conditions, adhering to prescribed medications, and attending regular check-ups is essential in preventing kidney disease progression (Thomas et al., 2019).
Patient education also plays a vital role in improving outcomes for individuals with existing kidney disease. Teaching patients about the importance of medication adherence, dietary restrictions, and recognizing the signs of worsening kidney function can empower them to take an active role in managing their condition. Additionally, providing support for lifestyle changes, such as smoking cessation and weight management, can improve overall health and reduce the burden of kidney disease (Kalantar-Zadeh et al., 2020).
Conclusion
Kidney disease is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the causes, stages, and symptoms of kidney disease is essential for early diagnosis and effective treatment. By managing underlying conditions such as diabetes and hypertension, healthcare providers can help slow the progression of chronic kidney disease. Treatment options range from medications and dietary changes in the early stages to dialysis and kidney transplantation in advanced disease. Prevention and patient education remain critical components in reducing the incidence and burden of kidney disease, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life. (Kidney Disorder/Disease)
References
Bellomo, R., Kellum, J. A., & Ronco, C. (2019). Acute kidney injury. Lancet, 394(10212), 1949-1964. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32563-2
Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Jafar, T. H., Nitsch, D., Neuen, B. L., & Perkovic, V. (2020). Chronic kidney disease. Lancet, 395(10223), 709-733. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32977-0
Levey, A. S., Coresh, J., Tighiouart, H., Inker, L. A., & Matsushita, K. (2020). GFR decline as an end point for clinical trials in CKD: A scientific workshop sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation and the US Food and Drug Administration. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 75(4), 474-485. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.11.007
Luyckx, V. A., Tonelli, M., & Stanifer, J. W. (2021). The global burden of kidney disease and the sustainable development goals. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 99(6), 406-415. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.20.269944
Thomas, B., Matsushita, K., Abate, K. H., Al-Aly, Z., Ärnlöv, J., Asayama, K.,… & Murray, C. J. (2019). Global cardiovascular and renal outcomes of reduced GFR. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology,
Do you need a similar assignment done for you from scratch? Order now!
Use Discount Code "Newclient" for a 15% Discount!