Study of manometry and polarography
Study of manometry and polarography
Manometry refers to measuring of pressure by use of the manometer device. Examples of manometry activities include; Esophageal manometry, is carried out to determine movements and muscle pressure in the esophagus when evaluating achalasia (smooth muscle fibers failure to relax), the doctors can determine the ability of the esophagus to move food to the stomach, forecast the reason behind you experiencing a digestive problem and know the processes of digesting and swallowing. Normally administered to people with swallowing difficulties and pain, heartburn and chest pain; the anal manometry, involves measuring the pressure the anal sphincter produces. Anal manometry is beneficial when evaluating anal and fecal incompetence and incontinence respectively. (Study of manometry and polarography)
Manometry operation theory
Manometry involves pressure measurement on the different areas in the GI-tract. Its operation involves use of a catheter with transducers filled with a liquid or in solid state (Ghosh, Pandolfino, Zhang, Jarosz, & Kahrilas, (2006). The catheter is passed through the mouth or anal into the canal of part to be studied. The operation is performed more so to evaluate disorders that cannot be explained by other studies. This disorder can be of the esophagus, duodenum, stomach, anal and rectal sphincters which give minor discomforts but have very little complications. A patient undergoing manometric tests is accustomed to several restrictions like, they are not allowed to eat anything past midnight. (Study of manometry and polarography)
Instrument used in manometric study
A manometer is widely used since it can measure and at the same time indicate the pressure, it uses a liquid column in its measurements. There are various types of manometers, the U-Tube manometer, two types; differential and inverted U-Tube manometers, the micro manometer, and the inclined manometer. The Bourdon gauge instrument is also commonly used, it operates mechanically and can also measure and indicate pressure. A vacuum gauge is also used, it measures the pressure below ambient atmospheric pressure. Other methods used to measure evolution of pressure involve sensors, the sensors are used in transmitting the pressure readings to a control system. (Study of manometry and polarography)
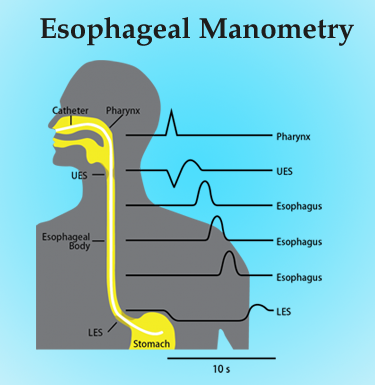
Types of manometry
Manometry is classified into three major categories, esophageal manometry, anorectal manometry, rhinomanometry. Esophageal test is carried out in patients experiencing heartburn, swallowing difficulties, and having chest and stomach pains. It involves two types of tests which are determined by your instructing physician. The standard manometry is the first test, it entails examining the functioning of the esophagus muscles and how effective the valve between the stomach and the esophagus is. The procedure involves inserting a tube in an anesthetized nose and pulling the tube back slowly through the esophagus, swallows with water are also undertaken. The second test is the impedance manometry which works closely as the standard manometry but involves assessment of bolus movements in the esophagus. The procedure involves a tube which is passed into the esophagus, performing swallows with saline and undertaking swallows with applesauce.
Anorectal manometry is performed by a gastroenterologist or any other assistant with special training. The pressure produced by the anal and rectal sphincter is measured by a transducer attached to a tube which is inserted into the anal canal and pulled slowly. The relaxation and contraction of the anal and rectal sphincter controls the bowel movements. The procedure can be performed alternatively by use of a metal cylinder that has three balloons attached to it to measure the pressure. Anorectal manometry is undertaken to determine anal canal functioning and understand the reasons for chronic constipation occurring, used as a treatment in restructuring contraction of anal muscles in those people with fecal inconsistency.
Rhinomanometry is carried out to evaluate the airflow in the nasal canal. The procedure involves a probe which is placed at the end of a nostril and attached by a tape. Masks are used in the test to cover the faces of patients who breath in severally through their noses. A sensor placed at the back of the cavity is sometimes used to check on the airflow and report the observation to a computer. (Study of manometry and polarography)
Applications of manometry
Esophageal manometry is applied clinically to patients with GERD and it involves pH monitoring. Extended esophageal pH monitoring is used to manage patients having symptoms which are typical or atypical and are under the standard therapy for GERD. This test is also applicable in monitoring abnormal reflux in a person without esophagitis being examined for anti-reflux surgery. The multichannel intraluminal impedance is a technic used to evaluate movements of the bolus in the esophagus. Its information relevance is expanded by combining it with manometry or the pH monitoring. Manometry is also applied when identifying non-functionality of the gastrointestinal tract. Problems in the GI tract involving smooth muscles and extrinsic nerves may be detected by measuring the pressure inside the tract and examining the phasic contraction of the tract. (Study of manometry and polarography)
Limitations of manometry
Analyzing esophageal disorder tracings is tiring, consumes a lot of time also and has different reader views. The procedure for undertaking esophageal test is uncomfortable and is accompanied by pain due to the anesthetization of the nostril through which the tube is inserted. Esophageal test has side effects like the, sore throats that are not severe, irritations and sinus problems. The patient may also suffer from nose bleeds. Anorectal manometry has side effects which include, slight discomfort and exposure to radiation associated with Defacograghy and Sitzmark test used when examining patients with chronic constipation. Nerve injuries may occur when the pudendal nerve testing is undertaken, this test is used to examine bladder and rectal sphincters. Intranasal corticosteroids like sildenafil citrate are used to treat nasal obstructions in people with allergic rhinitis. This treatment has associated side effects like sneezing. Itching of the nasal cavity and running nose. (Study of manometry and polarography)
What is polarography?
Polarography is an analysis method that involves subjecting a sample to electrolysis by use of specific electrodes and voltages of a given range, plotting a graph of current against voltage which shows procedures corresponding to a certain chemical and their concentration proportionality (Study of manometry and polarography)
Polarography theory
Polarography has a theory behind its operation, it includes the processes of oxidation, reduction, absorption, and catalysis. It is a subclass of voltammetry and involves voltammetric measurements in which convection mass transport determines their responses. Polarographic study involves examining solutions and electrode processes by applying the process of electrolysis. Electrolysis consists of polarized and un-polarized electrodes. The polarized electrode is formed by mercury which drops from a capillary tube more often. The electrode potential is changed linearly from the starting to the final potential and the graph produced has a sigmoid shape. The use of an electrode formed from a dropping mercury differentiates polarography from other voltammetry measurements. (Study of manometry and polarography)
Types of polarography
There are different types of polarography which are categorized in relation to their sensitivity and resolution; the classical polarography and the high-frequency polarography. (Study of manometry and polarography)
Applications of polarography
Polarography is applied in pharmaceutical analysis where it is used to differentiate reducible and oxidisable compounds (Zuman, (2006).). A base solution is used in which the sample to be studied is dissolved and placed in an electrolytic cell with a liquid mercury in a pool as anode and dropping mercury as cathode. Increasing voltage is applied in the cell and current measured with a galvanometer is used to evaluate the characteristics of the reducible compound. Changing the dropping mercury to be the anode helps determine the characteristics of the oxidisable compound. Polarography and voltammetry are applied in marine and aquatic chemistry; mercury is known to be toxic to aquatic life since it is dissolved in inland waters in small quantities that are hard to trace and when the water reacts with sediments there is a risk mercury entering the food chain of aquatic organisms, therefore polarography and voltammetry are used to detect mercury concentrations in aquatic environment. Direct current polarography in relation with other technics are used to determine derivatives of metals in ethylenebisdithiocarbamic acid where the stripping of a cathode is evaluated to be the most suitable methods (Busk, Horsman, Jakobsen, Keiding, van der Kogel, Bussink & Overgaard, (2008).) (Study of manometry and polarography)
limitations of polarography
The classical experiment of polarography that consists of quantitative analysis of different measurements has complications due to the rapidly changing electrode potentials applied to the electrode formed by the mercury drop in the whole experiment. The direct current polarography has limitations like, there is lack of clear explanations of the sigmoid curve; to distinguish two different waves and measure their potentials in a halfwave and limiting currents, they should have differing potentials above 200mV, instead the highest resolution is of about 50mV. Another limitation is the noise of the oscillations which increases after a substance is reduced hence making the calculation of other compounds undergoing reduction difficult. There are also some drawbacks in relation to the current needed to change the dropping mercury electrode potential, there is slight difference of the current and Faradaic current when a depolarizer concentration with number of moles ranging between 10-5 is used. (Study of manometry and polarography)
References
Von Renteln, D., Inoue, H., Minami, H., Werner, Y. B., Pace, A., Kersten, J. F., … & Fuchs, K. H. (2012). Peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia: a prospective single center study. The American journal of gastroenterology, 107(3), 411-417. 10.1038/ajg.2011.388
Ghosh, S. K., Pandolfino, J. E., Zhang, Q., Jarosz, A., & Kahrilas, P. J. (2006). Deglutitive upper esophageal sphincter relaxation: a study of 75 volunteer subjects using solid-state high-resolution manometry. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 291(3), G525-G531.
Pandolfino, J. E., Ghosh, S. K., Zhang, Q., Jarosz, A., Shah, N., & Kahrilas, P. J. (2006). Quantifying EGJ morphology and relaxation with high-resolution manometry: a study of 75 asymptomatic volunteers. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 290(5), G1033-G1040.
Busk, M., Horsman, M. R., Jakobsen, S., Keiding, S., van der Kogel, A. J., Bussink, J., & Overgaard, J. (2008). Imaging hypoxia in xenografted and murine tumors with 18 F-fluoroazomycin arabinoside: a comparative study involving microPET, autoradiography, pO 2-polarography, and fluorescence microscopy. International Journal of Radiation Oncology* Biology* Physics, 70(4), 1202-1212.
Zuman, P. (2006). Principles of applications of polarography and voltammetry in the analysis of drugs. FABAD Journal of Pharmaceutical Science, 31, 97115.