Nursing Paper Example on Type 1 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Overview
Nursing Paper Example on Type 1 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Overview
Causes
Type 1 diabetes is a multifactorial disease with a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. While the exact cause remains uncertain, several contributing factors have been identified through extensive research.
Genetic Predisposition: Genetic susceptibility plays a significant role in the development of type 1 diabetes. Individuals with specific human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes, particularly those carrying certain variants of the HLA-DR and HLA-DQ genes, have an increased risk of developing the condition. These genes encode proteins involved in immune regulation, making individuals more susceptible to autoimmune responses targeting pancreatic beta cells.
Environmental Triggers: Environmental factors, such as viral infections and dietary factors, are believed to trigger the onset of type 1 diabetes in genetically predisposed individuals. Viral infections, particularly enteroviruses and Coxsackievirus, have been implicated in initiating autoimmune responses by mimicking pancreatic antigens, leading to the activation of autoreactive T cells. Additionally, dietary factors, such as early exposure to cow’s milk or gluten during infancy, may increase the risk of developing type 1 diabetes in susceptible individuals.
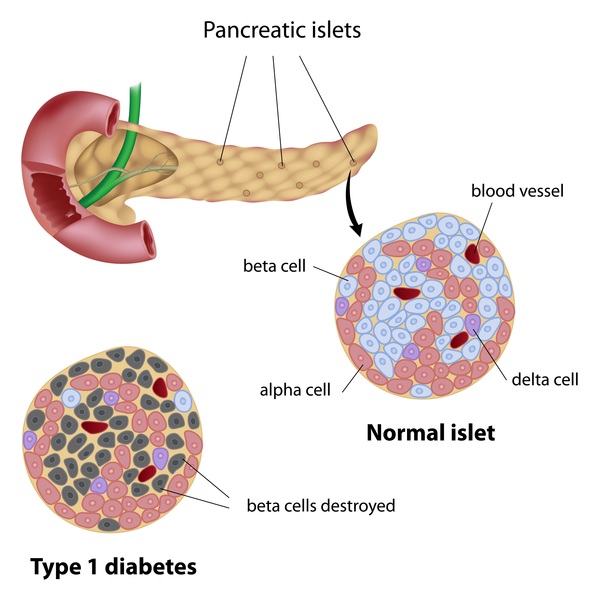
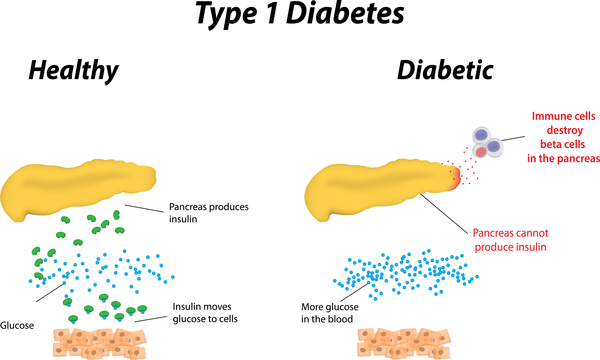
Immunological Dysfunction: Type 1 diabetes is characterized by an autoimmune response, where the body’s immune system mistakenly targets and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This autoimmune destruction is mediated by autoreactive T cells, which infiltrate the pancreatic islets and initiate an inflammatory cascade. The exact triggers that initiate this autoimmune response are not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and dysregulation of immune tolerance mechanisms.
Type 1 diabetes is a complex disease with a multifaceted etiology involving genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and immunological dysfunction. Understanding these contributing factors is essential for early detection, prevention, and targeted therapeutic interventions aimed at preserving pancreatic beta cell function and improving outcomes for individuals with type 1 diabetes. (Nursing Paper Example on Type 1 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Overview)
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes is crucial for early diagnosis and prompt management. The onset of symptoms is often rapid and may progress rapidly if left untreated.
Polyuria and Polydipsia: Excessive thirst (polydipsia) and frequent urination (polyuria) are hallmark symptoms of type 1 diabetes. The kidneys attempt to eliminate excess glucose from the bloodstream by excreting it in the urine, leading to increased urine production and subsequent dehydration, triggering thirst.
Unexplained Weight Loss: Rapid and unexplained weight loss is a common symptom of type 1 diabetes, particularly in children and adolescents. The body’s inability to utilize glucose for energy due to insulin deficiency results in the breakdown of muscle and fat stores, leading to weight loss despite increased appetite and food intake.
Fatigue and Weakness: Fatigue and weakness are common complaints among individuals with untreated type 1 diabetes. Insulin deficiency impairs glucose uptake by cells, resulting in reduced energy production and feelings of fatigue and weakness.
Blurred Vision: Elevated blood sugar levels can lead to changes in the shape of the lens in the eye, causing temporary blurring of vision. Blurred vision is often one of the early symptoms of undiagnosed type 1 diabetes and typically resolves with proper management of blood sugar levels.
Ketoacidosis: In severe cases of untreated type 1 diabetes, the body may enter a state of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is a life-threatening condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, ketone buildup in the bloodstream, dehydration, and metabolic acidosis. Symptoms of DKA include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fruity-smelling breath, and confusion.
Recognizing these signs and symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment to prevent complications and improve outcomes for individuals with type 1 diabetes. Early intervention can help prevent life-threatening complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis and reduce the risk of long-term complications associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels. (Nursing Paper Example on Type 1 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Overview)
Etiology
The etiology of type 1 diabetes is complex and multifactorial, involving a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and immunological dysregulation.
Genetic Predisposition: Genetic susceptibility plays a significant role in the development of type 1 diabetes. Certain human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes, particularly HLA-DR3 and HLA-DR4, are strongly associated with an increased risk of developing the condition. These genes encode proteins involved in immune regulation, making individuals carrying specific variants more susceptible to autoimmune responses targeting pancreatic beta cells.
Environmental Triggers: Environmental factors, such as viral infections and dietary factors, are believed to trigger the onset of type 1 diabetes in genetically predisposed individuals. Viral infections, particularly enteroviruses and Coxsackievirus, have been implicated in initiating autoimmune responses by mimicking pancreatic antigens, leading to the activation of autoreactive T cells. Additionally, dietary factors, such as early exposure to cow’s milk or gluten during infancy, may increase the risk of developing type 1 diabetes in susceptible individuals.
Immunological Dysregulation: Type 1 diabetes is characterized by an autoimmune response, where the body’s immune system mistakenly targets and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This autoimmune destruction is mediated by autoreactive T cells, which infiltrate the pancreatic islets and initiate an inflammatory cascade. The exact triggers that initiate this autoimmune response are not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and dysregulation of immune tolerance mechanisms.
Understanding the etiology of type 1 diabetes is essential for identifying individuals at risk, developing targeted prevention strategies, and advancing therapeutic interventions aimed at preserving pancreatic beta cell function and improving outcomes for individuals with the condition. Further research into the genetic and environmental factors contributing to type 1 diabetes is necessary to unravel the complexities of this disease and develop more effective treatment approaches. (Nursing Paper Example on Type 1 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Overview)
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of type 1 diabetes involves a complex interplay of genetic, immunological, and metabolic factors, ultimately leading to the destruction of pancreatic beta cells and insulin deficiency.
Autoimmune Destruction of Beta Cells: Type 1 diabetes is primarily characterized by an autoimmune response in which the body’s immune system mistakenly targets and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This autoimmune destruction is mediated by autoreactive T cells, which infiltrate the pancreatic islets and initiate an inflammatory cascade. As a result, pancreatic beta cells are gradually destroyed, leading to a progressive decline in insulin secretion.
Insulin Deficiency and Hyperglycemia: The destruction of pancreatic beta cells results in an absolute deficiency of insulin, impairing the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin plays a crucial role in facilitating glucose uptake by cells, particularly in muscle, liver, and adipose tissue. In the absence of insulin, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia.
Metabolic Disturbances: Hyperglycemia triggers a series of metabolic disturbances, including increased hepatic glucose production, impaired glucose uptake by peripheral tissues, and accelerated breakdown of fats and proteins for energy. The inability of cells to utilize glucose for energy production leads to metabolic derangements and cellular dysfunction.
Ketosis and Diabetic Ketoacidosis: In severe cases of untreated type 1 diabetes, the body may enter a state of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) due to the breakdown of fats for energy in the absence of adequate insulin. Ketone bodies, such as acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate, accumulate in the bloodstream, leading to metabolic acidosis and potentially life-threatening complications.
Understanding the pathophysiology of type 1 diabetes is essential for developing targeted therapeutic interventions aimed at preserving pancreatic beta cell function, restoring insulin secretion, and improving outcomes for individuals with the condition. Further research into the underlying mechanisms driving autoimmune destruction and metabolic dysregulation in type 1 diabetes is necessary to advance our understanding and develop more effective treatment strategies. (Nursing Paper Example on Type 1 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Overview)
DSM-5 Diagnosis
The diagnosis of type 1 diabetes is based on clinical symptoms, laboratory tests, and criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5). The DSM-5 criteria provide a standardized framework for identifying and categorizing psychiatric disorders, including diabetes-related conditions.
Elevated Blood Glucose Levels: One of the primary criteria for diagnosing type 1 diabetes is the presence of elevated blood glucose levels. Fasting plasma glucose levels ≥126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) on two separate occasions are indicative of diabetes mellitus.
Presence of Ketones: In addition to elevated blood glucose levels, the presence of ketones in the urine or blood is a diagnostic indicator of type 1 diabetes. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fats for energy in the absence of sufficient insulin. Ketone bodies, such as beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate, can be detected using urine or blood tests.
Symptoms of Hyperglycemia: Clinical symptoms of hyperglycemia, such as polyuria (excessive urination), polydipsia (excessive thirst), unexplained weight loss, and fatigue, are important diagnostic criteria for type 1 diabetes. The presence of these symptoms, along with elevated blood glucose levels and ketones, supports the diagnosis of the condition.
Additional Diagnostic Tests: Additional diagnostic tests may be performed to confirm the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes and assess its severity. These tests may include measurement of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, which provide an estimate of average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months, and assessment of pancreatic autoantibodies, such as glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies and insulin autoantibodies, which are indicative of autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells.
Overall, the DSM-5 criteria for diagnosing type 1 diabetes provide a standardized framework for healthcare professionals to identify and categorize the condition based on clinical symptoms, laboratory tests, and diagnostic criteria. Early detection and timely diagnosis are essential for initiating appropriate treatment and preventing complications in individuals with type 1 diabetes. (Nursing Paper Example on Type 1 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Overview)